Exploring Telehealth Devices: Transforming Modern Healthcare
Telehealth devices have revolutionized the healthcare industry by enabling remote patient monitoring, consultation, and management. These devices provide a bridge between patients and healthcare providers, ensuring continuous and efficient care, especially for those with chronic conditions or in remote areas. This article delves into the various types of telehealth devices, their functionalities, benefits, challenges, and future prospects in the healthcare landscape.
The Rise of Telehealth
Telehealth refers to the use of digital information and communication technologies to access healthcare services remotely and manage healthcare. It encompasses a wide range of technologies and applications, from video consultations to remote patient monitoring (RPM) devices. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of telehealth, highlighting its potential to improve healthcare accessibility and efficiency.
Types of Telehealth Devices
Telehealth devices vary in their functionalities and applications. Here are some of the most common types:
- Remote Patient Monitoring Devices (RPM): RPM devices track vital signs and health metrics, transmitting data to healthcare providers for continuous monitoring. Common RPM devices include:
- Blood Pressure Monitors: Measure blood pressure and transmit readings to healthcare providers.
- Glucose Monitors: Track blood glucose levels in real-time, essential for diabetes management.
- Pulse Oximeters: Measure blood oxygen levels and pulse rate, useful for patients with respiratory conditions.
- Heart Rate Monitors: Track heart rate and rhythm, helping detect arrhythmias and other cardiac conditions.
- Weight Scales: Monitor weight changes, crucial for managing conditions like heart failure.
- Telehealth Consultation Tools: These tools facilitate virtual consultations between patients and healthcare providers. They include:
- Video Conferencing Platforms: Enable face-to-face interactions, allowing for visual examinations and discussions.
- Telehealth Apps: Provide a platform for scheduling appointments, sharing medical records, and messaging healthcare providers.
- Wearable Devices: Wearables track various health metrics and can be integrated with telehealth platforms. Common wearables include:
- Smartwatches: Monitor heart rate, activity levels, sleep patterns, and other health metrics.
- Fitness Trackers: Track physical activity, sleep, and other health-related metrics.
- Smart Home Health Devices: These devices integrate with smart home systems to monitor health metrics and provide alerts. Examples include:
- Smart Thermometers: Track body temperature and detect fevers.
- Smart Pill Dispensers: Remind patients to take medications and track adherence.
How Telehealth Devices Work
Telehealth devices use a combination of sensors, connectivity, and software to collect, transmit, and analyze health data. Here’s how they typically function:
- Data Collection: Devices use sensors to measure health metrics such as heart rate, blood pressure, glucose levels, and more.
- Data Transmission: Collected data is transmitted to healthcare providers via secure internet connections. Some devices use Bluetooth to connect to smartphones, which then upload the data to cloud-based platforms.
- Data Analysis: Healthcare providers analyze the transmitted data, using algorithms and AI to detect patterns and anomalies.
- Feedback and Intervention: Based on the analysis, healthcare providers offer feedback, adjust treatment plans, or intervene if necessary. Patients can also access their data and receive notifications or alerts.
Benefits of Telehealth Devices
Telehealth devices offer numerous benefits for patients, healthcare providers, and the healthcare system as a whole:
- Increased Access to Care: Telehealth devices make healthcare accessible to individuals in remote or underserved areas, eliminating geographical barriers.
- Continuous Monitoring: Continuous monitoring allows for early detection of health issues, enabling timely intervention and preventing complications.
- Convenience and Comfort: Patients can receive care from the comfort of their homes, reducing the need for frequent clinic visits and hospitalizations.
- Improved Chronic Disease Management: For patients with chronic conditions, telehealth devices facilitate better disease management through regular monitoring and feedback.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Telehealth can reduce healthcare costs by decreasing hospital admissions, emergency visits, and travel expenses for patients.
- Enhanced Patient Engagement: Patients are more engaged in their health management, with access to their data and regular interactions with healthcare providers.
- Data-Driven Insights: The data collected from telehealth devices can be used for research, helping improve treatments and healthcare policies.
Challenges and Considerations
While telehealth devices offer significant advantages, there are also challenges and considerations to address:
- Data Privacy and Security: Ensuring the privacy and security of patient data is paramount. Telehealth devices must comply with regulations like HIPAA to protect sensitive information.
- Technology Adoption and Literacy: Patients and healthcare providers need to be comfortable with using telehealth devices. Training and support are essential for successful adoption.
- Connectivity Issues: Reliable internet connectivity is crucial for telehealth. In areas with poor connectivity, telehealth services may be limited.
- Accuracy and Reliability: The accuracy and reliability of telehealth devices must be validated to ensure they provide accurate and useful data.
- Integration with Healthcare Systems: Integrating telehealth data with existing electronic health records (EHRs) can be challenging but is necessary for comprehensive care.
- Regulatory and Reimbursement Issues: Regulatory frameworks and reimbursement policies need to evolve to support the widespread adoption of telehealth services.
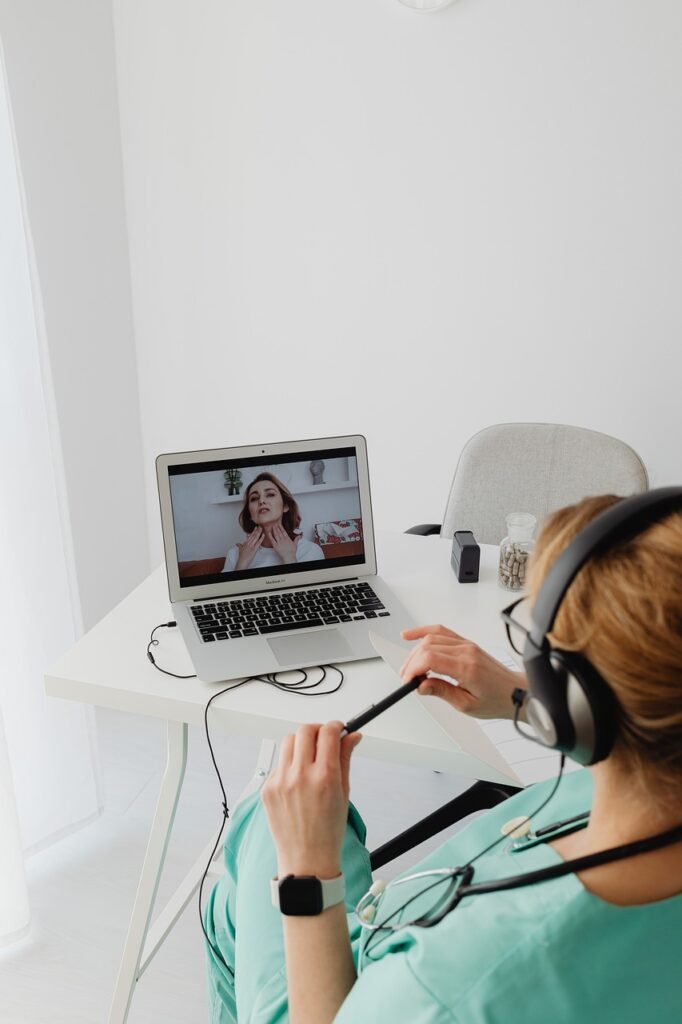

Best Practices for Using Telehealth Devices
To maximize the benefits of telehealth devices, it’s important to follow best practices:
- Choose the Right Device: Select devices that meet your specific health monitoring needs and have a good reputation for accuracy and reliability.
- Ensure Data Privacy: Use devices and platforms that prioritize data privacy and security. Understand how your data is collected, stored, and used.
- Regular Monitoring and Reporting: Use the devices consistently and report any issues or concerns to your healthcare provider promptly.
- Stay Informed and Trained: Stay informed about how to use the devices properly and seek training or support if needed.
- Collaborate with Healthcare Providers: Share your data with your healthcare provider and collaborate on your treatment plan.
The Future of Telehealth Devices
The future of telehealth devices looks promising, with advancements in technology paving the way for more sophisticated and accessible solutions. Here are some trends to watch for:
- Integration with AI and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning algorithms will enhance data analysis, providing more accurate and personalized insights.
- Wearable Biosensors: Advances in biosensor technology will enable continuous monitoring of a wider range of biomarkers, providing deeper insights into health and wellness.
- Telehealth Platforms: Comprehensive telehealth platforms will integrate data from various devices and sources, offering a holistic view of health and personalized recommendations.
- Improved User Experience: Future telehealth devices will focus on improving the user experience through better design, more intuitive interfaces, and seamless integration with daily routines.
- Enhanced Connectivity: The expansion of 5G networks will improve connectivity and enable real-time data transmission, enhancing the effectiveness of telehealth services.
- Regulatory Support: Evolving regulatory frameworks and reimbursement policies will support the widespread adoption of telehealth services.
Conclusion
Telehealth devices are transforming healthcare by enabling remote monitoring, consultation, and management. They offer numerous benefits, including increased access to care, continuous monitoring, and improved chronic disease management. However, challenges such as data privacy, technology adoption, and connectivity must be addressed to realize their full potential. As technology continues to advance, the future of telehealth devices holds even greater promise, offering more sophisticated, accurate, and accessible solutions for a healthier world. By leveraging the power of telehealth devices, healthcare providers and patients can work together to achieve better health outcomes and a more efficient healthcare system.