The Comprehensive Guide to Blood Pressure Monitors
Blood pressure monitors are essential tools for managing cardiovascular health. These devices provide critical data that helps individuals monitor their blood pressure, enabling early detection of hypertension and other heart-related conditions. This article explores the evolution, technology, benefits, challenges, and future of blood pressure monitors, offering a comprehensive understanding of their role in modern healthcare.
The Evolution of Blood Pressure Monitors
The measurement of blood pressure began in the early 18th century, but it wasn’t until the late 19th century that devices resembling modern blood pressure monitors were developed. The first non-invasive blood pressure monitor, the sphygmomanometer, was invented by Samuel Siegfried Karl Ritter von Basch in 1881. This device used a mercury column and an inflatable cuff to measure systolic and diastolic pressure.
In the early 20th century, Dr. Nikolai Korotkoff developed the auscultatory method, which involved listening to the Korotkoff sounds with a stethoscope while deflating the cuff. This method remains a gold standard for blood pressure measurement. The development of electronic blood pressure monitors in the 1970s marked a significant advancement, offering more accurate and user-friendly options for both clinical and home use.
How Blood Pressure Monitors Work
Modern blood pressure monitors use either the auscultatory method or the oscillometric method to measure blood pressure.
- Auscultatory Method: This traditional method involves placing a cuff around the upper arm and inflating it until the blood flow is restricted. As the cuff deflates, a stethoscope is used to listen for the Korotkoff sounds. The pressure at which these sounds first appear is the systolic pressure, and the pressure at which they disappear is the diastolic pressure.
- Oscillometric Method: Most automatic blood pressure monitors use this method. The device detects oscillations in the arterial wall caused by blood flow as the cuff inflates and deflates. These oscillations are then analyzed by the device to calculate systolic and diastolic pressure. Oscillometric monitors are easy to use, making them popular for home monitoring.
Types of Blood Pressure Monitors
Blood pressure monitors come in various types, each suited for different needs and preferences.
- Manual Monitors: These include aneroid monitors, which require the use of a stethoscope and manual inflation of the cuff. They are typically used by healthcare professionals due to their accuracy and reliability.
- Automatic Monitors: These are the most common type of blood pressure monitors for home use. They are easy to operate, with automatic inflation and deflation of the cuff and digital readouts of blood pressure readings.
- Wrist Monitors: These devices measure blood pressure at the wrist rather than the upper arm. While more compact and portable, they can be less accurate due to positioning errors and are generally recommended for individuals who find upper arm monitors uncomfortable.
- Ambulatory Monitors: These monitors are used for 24-hour blood pressure monitoring. They are worn continuously and take readings at regular intervals throughout the day and night, providing a comprehensive picture of an individual’s blood pressure patterns.
- Smart Monitors: Integrated with smartphone apps, these monitors offer advanced features such as data tracking, analysis, and sharing with healthcare providers. They are ideal for tech-savvy individuals who want to monitor their blood pressure trends over time.
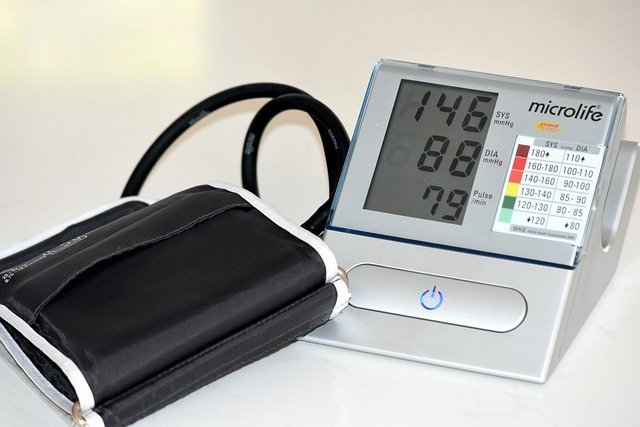
Benefits of Using Blood Pressure Monitors
Blood pressure monitors offer numerous benefits for managing cardiovascular health.
- Early Detection of Hypertension: Regular monitoring allows for the early detection of high blood pressure, which is often asymptomatic. Early intervention can prevent complications such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney damage.
- Better Management of Existing Conditions: For individuals with diagnosed hypertension or other cardiovascular conditions, regular monitoring helps in managing the condition more effectively. It allows for timely adjustments to medication and lifestyle changes based on accurate data.
- Empowerment and Awareness: Blood pressure monitors empower individuals to take control of their health. By providing real-time data, these devices increase awareness of how lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and stress affect blood pressure.
- Convenience and Accessibility: Home blood pressure monitors make it easy for individuals to monitor their blood pressure without frequent visits to the doctor. This is particularly beneficial for those with mobility issues or busy schedules.
- Comprehensive Health Tracking: Advanced blood pressure monitors, especially smart monitors, allow users to track their readings over time, providing valuable insights into their overall cardiovascular health.
Challenges and Considerations
While blood pressure monitors offer significant benefits, there are also challenges and considerations to keep in mind.
- Accuracy: The accuracy of blood pressure monitors can be affected by factors such as cuff size, placement, and user technique. It’s essential to follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully and ensure the device is calibrated regularly.
- User Error: Inaccurate readings can result from improper use of the monitor, such as incorrect cuff placement or movement during measurement. Education and training on correct usage are crucial to obtaining reliable readings.
- Cost: High-quality blood pressure monitors, especially those with advanced features, can be expensive. Users should consider their specific needs and budget when selecting a device, ensuring they choose one that provides the necessary features without overspending.
- Data Interpretation: While blood pressure monitors provide raw data, interpreting this data accurately requires some knowledge. Users should consult with healthcare professionals to understand their readings and make informed decisions.
- Dependence on Technology: Over-reliance on blood pressure monitors can sometimes lead to an overemphasis on numbers rather than overall health and well-being. It’s important for users to use these devices as tools for guidance rather than becoming overly fixated on individual readings.
Popular Blood Pressure Monitors
Several brands are renowned for their reliable and accurate blood pressure monitors.
- Omron: A leading brand in blood pressure monitoring, Omron offers a wide range of devices, from basic models to advanced smart monitors. The Omron Platinum Blood Pressure Monitor is particularly well-regarded for its accuracy and connectivity features.
- Withings: Known for their smart health devices, Withings offers blood pressure monitors that integrate seamlessly with their health ecosystem. The Withings BPM Connect provides easy-to-read results and wireless connectivity for tracking data over time.
- A&D Medical: A&D Medical offers a variety of blood pressure monitors, including upper arm and wrist models. Their devices are known for their accuracy and user-friendly design.
- Beurer: Beurer produces high-quality blood pressure monitors with a focus on ease of use and reliable performance. Their Beurer BM55 model includes advanced features such as arrhythmia detection and average value calculation.
- iHealth: iHealth offers smart blood pressure monitors that connect to smartphones for easy data tracking and sharing. The iHealth Clear Blood Pressure Monitor provides color-coded feedback and cloud-based data storage.
The Future of Blood Pressure Monitors
The future of blood pressure monitors is promising, with ongoing advancements in technology expected to bring even more sophisticated and useful features.
- Enhanced Sensors: Future blood pressure monitors may include advanced sensors capable of measuring additional health metrics, such as blood oxygen levels and arterial stiffness. These enhancements will provide users with a more comprehensive view of their cardiovascular health.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI and machine learning algorithms will likely play a greater role in analyzing blood pressure data and providing personalized recommendations. This will help users make more informed decisions about their health and manage their conditions more effectively.
- Integration with Health Care: Blood pressure monitors may become more integrated with the healthcare system, allowing for seamless sharing of data with healthcare providers. This will enable more proactive and personalized medical care, improving health outcomes.
- Wearable Technology: As wearable technology continues to evolve, we may see the development of more compact and comfortable blood pressure monitors that can be worn continuously. This will provide users with continuous blood pressure monitoring and real-time alerts for any abnormalities.
- Telehealth Integration: With the rise of telehealth, blood pressure monitors will play a crucial role in remote patient monitoring. This will allow healthcare providers to monitor patients’ blood pressure in real-time, providing timely interventions and reducing the need for frequent in-person visits.
Conclusion
Blood pressure monitors have evolved significantly from their early days as bulky medical devices. Today, they offer a wealth of features and insights that can help individuals lead healthier, more active lives. By providing accurate data, early detection of hypertension, and better management of existing conditions, these devices have become invaluable tools for both clinical and home use. As technology continues to advance, the potential for even more sophisticated and beneficial blood pressure monitors is vast, promising an exciting future for this rapidly evolving field.
4o