Understanding Glucose Meters: A Comprehensive Guide
Glucose meters, also known as glucometers, are indispensable tools for individuals managing diabetes. These compact devices enable people to monitor their blood glucose levels regularly, ensuring effective management of the condition. Given the rising prevalence of diabetes worldwide, understanding the functionalities, types, and importance of glucose meters is crucial. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of glucose meters, exploring their evolution, working mechanism, types, and the role they play in diabetes management.
The Evolution of Glucose Meters
The journey of glucose meters dates back to the 1960s when the first blood glucose test was developed. Initially, these tests were cumbersome and required laboratory equipment. The early meters were large, expensive, and primarily used in hospitals. The evolution of technology over the decades has significantly transformed glucose meters, making them more accessible and user-friendly.
In the 1970s, the first portable glucose meter was introduced, revolutionizing diabetes management. This innovation allowed individuals to monitor their blood glucose levels at home, providing a sense of independence and control over their condition. The subsequent decades witnessed significant advancements in technology, leading to the development of smaller, more accurate, and easier-to-use glucose meters.
How Glucose Meters Work
Glucose meters operate on a simple principle: they measure the concentration of glucose in a small sample of blood. Here’s a step-by-step overview of how a typical glucose meter works:
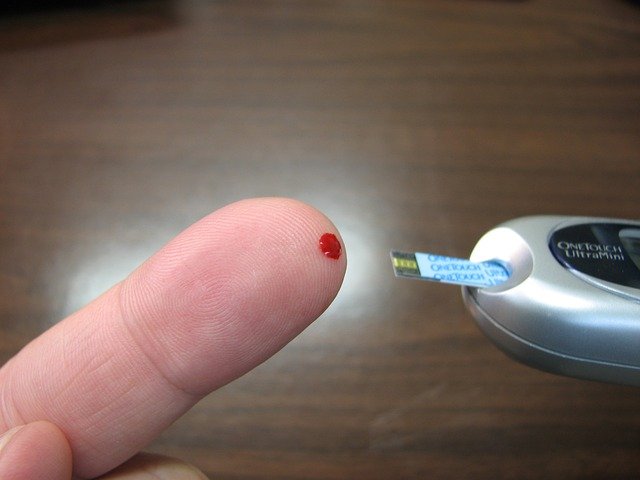
- Blood Sample Collection: A small drop of blood is obtained using a lancet, a tiny needle-like device. The blood is usually drawn from a fingertip.
- Application to Test Strip: The drop of blood is applied to a test strip, which contains chemicals that react with glucose.
- Insertion into Meter: The test strip is then inserted into the glucose meter, which analyzes the blood sample.
- Electrochemical Reaction: Inside the meter, an electrochemical reaction occurs between the blood glucose and the chemicals on the strip. This reaction generates an electrical current.
- Measurement and Display: The meter measures the electrical current, which is proportional to the glucose concentration in the blood. The result is displayed on the screen within seconds.
Types of Glucose Meters
Glucose meters come in various types, each catering to different needs and preferences. Understanding these types can help individuals choose the most suitable device for their diabetes management.
- Standard Blood Glucose Meters: These are the most common type of glucose meters. They require a small drop of blood from a fingertip and provide results within seconds. They are portable, user-friendly, and widely available.
- Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs): CGMs are advanced devices that provide real-time glucose readings throughout the day and night. They consist of a sensor inserted under the skin, which measures interstitial glucose levels continuously. CGMs are particularly beneficial for individuals with type 1 diabetes or those with frequent glucose fluctuations.
- Flash Glucose Monitors: Similar to CGMs, flash glucose monitors use a sensor placed under the skin. However, instead of continuous readings, users need to scan the sensor with a reader to obtain their glucose levels. Flash glucose monitors offer a middle ground between standard meters and CGMs.
- Non-Invasive Glucose Meters: These meters do not require a blood sample. Instead, they use alternative methods such as infrared light or electromagnetic waves to measure glucose levels. While non-invasive meters are still in the developmental stage, they hold promise for pain-free glucose monitoring in the future.
Importance of Glucose Monitoring
Regular glucose monitoring is a cornerstone of diabetes management. It provides valuable insights into how lifestyle factors, such as diet, exercise, and medication, affect blood glucose levels. Here are some key reasons why glucose monitoring is crucial:
- Prevention of Hypoglycemia and Hyperglycemia: Monitoring blood glucose levels helps prevent hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), both of which can have severe health consequences.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Regular monitoring allows healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans based on individual glucose patterns, leading to better diabetes control.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: By tracking glucose levels, individuals can identify the impact of specific foods, physical activities, and stress on their blood sugar, enabling them to make informed lifestyle adjustments.
- Early Detection of Complications: Regular monitoring can help detect early signs of diabetes-related complications, such as neuropathy, retinopathy, and cardiovascular issues, allowing for timely intervention.
Features to Consider When Choosing a Glucose Meter
With numerous glucose meters available in the market, selecting the right one can be overwhelming. Here are some essential features to consider when choosing a glucose meter:
- Accuracy: The accuracy of the meter is paramount. Look for meters that meet the ISO (International Organization for Standardization) standards for accuracy.
- Ease of Use: Consider the user-friendliness of the meter. Features such as large display screens, simple navigation, and easy-to-handle test strips can enhance usability.
- Sample Size: Some meters require a smaller blood sample, which can be less painful and more convenient.
- Testing Speed: The time it takes for the meter to display the results is important, especially for individuals who need quick readings.
- Memory and Data Management: Many modern meters come with memory storage and connectivity options, allowing users to track their glucose trends over time and share data with healthcare providers.
- Cost: Consider the cost of the meter and the test strips, as they can vary significantly. Some meters may be more affordable initially but have expensive test strips.
- Special Features: Some meters offer additional features such as backlit screens, voice prompts, and alternative site testing, which can be beneficial for specific user needs.
Best Practices for Using Glucose Meters
To ensure accurate and reliable readings, it’s essential to follow best practices when using glucose meters:
- Wash Hands: Always wash hands with soap and water before testing to remove any substances that could affect the reading.
- Use Fresh Test Strips: Ensure that the test strips are not expired or damaged, as this can lead to inaccurate results.
- Calibrate the Meter: Some meters require calibration with a control solution to ensure accuracy. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for calibration.
- Proper Storage: Store the meter and test strips in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and moisture.
- Follow Manufacturer’s Instructions: Read and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for using the meter and test strips.
- Regular Maintenance: Clean the meter regularly as per the manufacturer’s guidelines to maintain its accuracy and longevity.
The Future of Glucose Meters
The future of glucose meters is promising, with ongoing research and technological advancements paving the way for more innovative and user-friendly devices. Here are some potential developments:
- Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring: Continued research into non-invasive methods could lead to the development of reliable, pain-free glucose meters, eliminating the need for blood samples.
- Integration with Wearable Technology: Future glucose meters may integrate seamlessly with wearable devices, providing continuous monitoring and real-time alerts on smartwatches or smartphones.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: The incorporation of AI and machine learning can enhance the accuracy of glucose meters and provide predictive insights, helping users manage their condition more effectively.
- Improved Sensor Technology: Advancements in sensor technology may lead to more accurate and long-lasting sensors for CGMs and flash glucose monitors.
- Personalized Diabetes Management: Future glucose meters may offer personalized recommendations based on individual glucose patterns, lifestyle factors, and genetic information.
Conclusion
Glucose meters have come a long way since their inception, evolving into indispensable tools for diabetes management. By providing accurate and timely information about blood glucose levels, these devices empower individuals to take control of their condition and make informed decisions about their health. As technology continues to advance, the future of glucose meters looks bright, promising even more innovative solutions for effective diabetes management. Whether through traditional blood glucose meters, continuous glucose monitors, or emerging non-invasive methods, the goal remains the same: to improve the quality of life for individuals with diabetes and help them lead healthier, more fulfilling lives.