Comprehensive Guide to Health Monitoring
Health monitoring is an essential aspect of modern healthcare, enabling individuals and healthcare providers to track various health parameters, detect potential issues early, and manage chronic conditions effectively. With advancements in technology, health monitoring has become more accessible, accurate, and comprehensive. This guide explores the importance of health monitoring, the types of devices and technologies available, and the benefits and challenges associated with their use.
The Importance of Health Monitoring
Health monitoring plays a crucial role in maintaining and improving overall health. Regular monitoring can help:
- Early Detection of Diseases: By tracking vital signs and other health parameters, potential health issues can be detected early, allowing for timely intervention and treatment.
- Management of Chronic Conditions: Individuals with chronic conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease can manage their health more effectively by monitoring relevant health metrics.
- Promotion of Healthy Lifestyles: Monitoring health parameters such as physical activity, sleep, and nutrition can encourage healthier lifestyle choices and behaviors.
- Empowerment of Patients: Health monitoring tools empower individuals to take a proactive role in managing their health, leading to better outcomes and enhanced well-being.
Types of Health Monitoring Devices and Technologies
Health monitoring encompasses a wide range of devices and technologies, each designed to track specific health parameters. Here are some of the most common types:
- Wearable Devices: Wearable devices like fitness trackers and smartwatches have gained immense popularity. They monitor physical activity, heart rate, sleep patterns, and other metrics. Examples include Fitbit, Apple Watch, and Garmin devices.
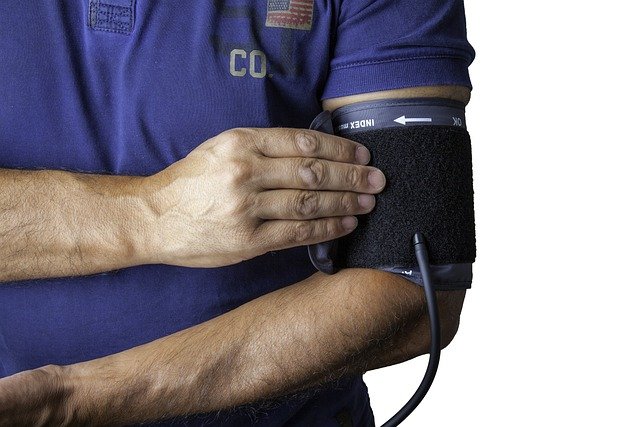
- Blood Pressure Monitors: These devices measure blood pressure and are essential for individuals with hypertension or cardiovascular conditions. They come in various forms, including wrist and upper-arm monitors.
- Glucose Meters: Glucose meters are used by individuals with diabetes to monitor blood sugar levels. Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) provide real-time data and insights into glucose trends.
- Pulse Oximeters: Pulse oximeters measure blood oxygen levels and pulse rate. They are especially useful for individuals with respiratory conditions and during high-altitude activities.
- Smart Scales: Smart scales measure weight, body fat percentage, muscle mass, and other body composition metrics. They sync with health apps to track progress over time.
- ECG Monitors: Electrocardiogram (ECG) monitors track the heart’s electrical activity, helping detect irregular heartbeats and other cardiac issues. Portable ECG devices can be used at home.
- Sleep Trackers: Sleep trackers monitor sleep patterns and provide insights into sleep quality and duration. They can be wearable or non-wearable devices.
- Smart Thermometers: These devices measure body temperature and often sync with health apps to track temperature trends and detect fevers early.
- Respiratory Monitors: These devices track breathing patterns and can be particularly useful for individuals with asthma, COPD, or other respiratory conditions.
How Health Monitoring Devices Work
Health monitoring devices use various sensors and technologies to collect data, which is then processed and analyzed to provide insights into health metrics. Here’s an overview of how some common devices work:
- Accelerometers and Gyroscopes: These sensors detect movement and orientation, enabling devices to track physical activity, steps taken, and sleep patterns.
- Optical Sensors: Optical sensors use light to measure heart rate, blood oxygen levels, and other metrics. They are commonly found in wearable devices like fitness trackers and smartwatches.
- Electrochemical Sensors: Glucose meters and other biosensors use electrochemical reactions to measure blood glucose levels and other biochemical markers.
- Pressure Sensors: Blood pressure monitors use pressure sensors to measure the force of blood against artery walls, providing systolic and diastolic pressure readings.
- Temperature Sensors: Smart thermometers and other devices use temperature sensors to measure body temperature accurately.
- Electrical Sensors: ECG monitors use electrical sensors to detect the heart’s electrical activity, providing detailed information about heart rhythms.
Benefits of Health Monitoring
The benefits of health monitoring are vast and impactful, influencing both individual health management and broader healthcare systems. Here are some key advantages:
- Personalized Healthcare: Health monitoring devices provide data that can be used to personalize healthcare plans, ensuring that treatments and interventions are tailored to individual needs.
- Proactive Health Management: Regular monitoring allows individuals to take proactive steps to maintain their health, such as adjusting diet, increasing physical activity, or seeking medical advice when necessary.
- Remote Monitoring: Health monitoring devices enable remote monitoring, allowing healthcare providers to track patients’ health metrics without the need for frequent in-person visits. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with chronic conditions.
- Data-Driven Insights: The data collected by health monitoring devices can be analyzed to identify trends, patterns, and potential health issues, leading to more informed decision-making.
- Enhanced Patient Engagement: Health monitoring tools engage patients in their own care, fostering a sense of responsibility and involvement in managing their health.
- Cost Savings: By detecting health issues early and enabling more efficient management of chronic conditions, health monitoring can reduce healthcare costs associated with hospitalizations and emergency care.
Challenges and Considerations
While health monitoring offers numerous benefits, there are also challenges and considerations to keep in mind:
- Accuracy and Reliability: The accuracy and reliability of health monitoring devices can vary. It’s important to choose reputable devices and validate their accuracy through clinical studies or comparisons with medical-grade equipment.
- Data Privacy and Security: Health monitoring devices collect sensitive personal health data. Ensuring the privacy and security of this data is crucial, especially with the rise of cyber threats.
- User Compliance: The effectiveness of health monitoring depends on user compliance. Individuals must consistently use the devices and follow recommendations for accurate and meaningful insights.
- Integration with Healthcare Systems: Integrating data from health monitoring devices into electronic health records (EHRs) and healthcare systems can be challenging but is essential for comprehensive care.
- Interpreting Data: The data collected by health monitoring devices can be complex. It’s important for users to understand how to interpret the data and when to seek medical advice.
- Cost and Accessibility: While many health monitoring devices are becoming more affordable, cost and accessibility can still be barriers for some individuals. Ensuring equitable access to these tools is important for improving public health.
Best Practices for Using Health Monitoring Devices
To maximize the benefits of health monitoring devices, it’s important to follow best practices:
- Choose the Right Device: Select devices that meet your specific health monitoring needs and have a good reputation for accuracy and reliability.
- Consistent Use: Use the devices consistently and as directed. Regular monitoring is essential for gathering accurate and meaningful data.
- Track Multiple Metrics: Consider tracking multiple health metrics to get a comprehensive view of your health. For example, monitor physical activity, sleep, and heart rate together.
- Use Data for Actionable Insights: Analyze the data collected to identify trends and patterns. Use this information to make informed decisions about your health and lifestyle.
- Consult Healthcare Providers: Share your health monitoring data with your healthcare provider. They can help interpret the data and provide guidance on managing your health.
- Prioritize Data Privacy: Ensure that the devices and apps you use have strong data privacy and security measures in place. Be aware of how your data is collected, stored, and used.
The Future of Health Monitoring
The future of health monitoring is bright, with ongoing advancements in technology promising even more sophisticated and accessible tools. Here are some trends to watch for:
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning algorithms can enhance the analysis of health data, providing more accurate predictions and personalized insights.
- Integration with Smart Home Devices: Health monitoring devices will increasingly integrate with smart home systems, enabling seamless tracking of health metrics and environmental factors that affect health.
- Wearable Biosensors: Advances in wearable biosensor technology will enable the continuous monitoring of a wider range of biomarkers, providing deeper insights into health and wellness.
- Telehealth and Remote Monitoring: The growth of telehealth will continue to drive the adoption of remote monitoring solutions, allowing for more efficient and convenient healthcare delivery.
- Holistic Health Platforms: Comprehensive health platforms will integrate data from various devices and sources, offering a holistic view of health and personalized recommendations for improvement.
Conclusion
Health monitoring is a powerful tool for enhancing individual health management and improving healthcare outcomes. By leveraging the latest technologies and following best practices, individuals can gain valuable insights into their health, detect potential issues early, and take proactive steps to maintain and improve their well-being. As technology continues to advance, the future of health monitoring holds even greater promise, offering more sophisticated, accurate, and accessible solutions for a healthier world. Whether through wearable devices, smart scales, or advanced biosensors, health monitoring is poised to play a central role in the future of healthcare.